Data Component API
The DataComponent API is currently experimental, and is additionally subject to change across versions.
The DataComponent API provides a version-specific interface for accessing and manipulating item data that is otherwise not representable by the ItemMeta API.
Through this API, you can read and modify properties of an item, so called data components, in a stable and object-oriented manner.
Introduction
What is a data component?
A data component represents a piece of data associated with an item. Vanilla items can have properties such as custom model data, container loot contents, banner patterns, or potion effects.
Structure
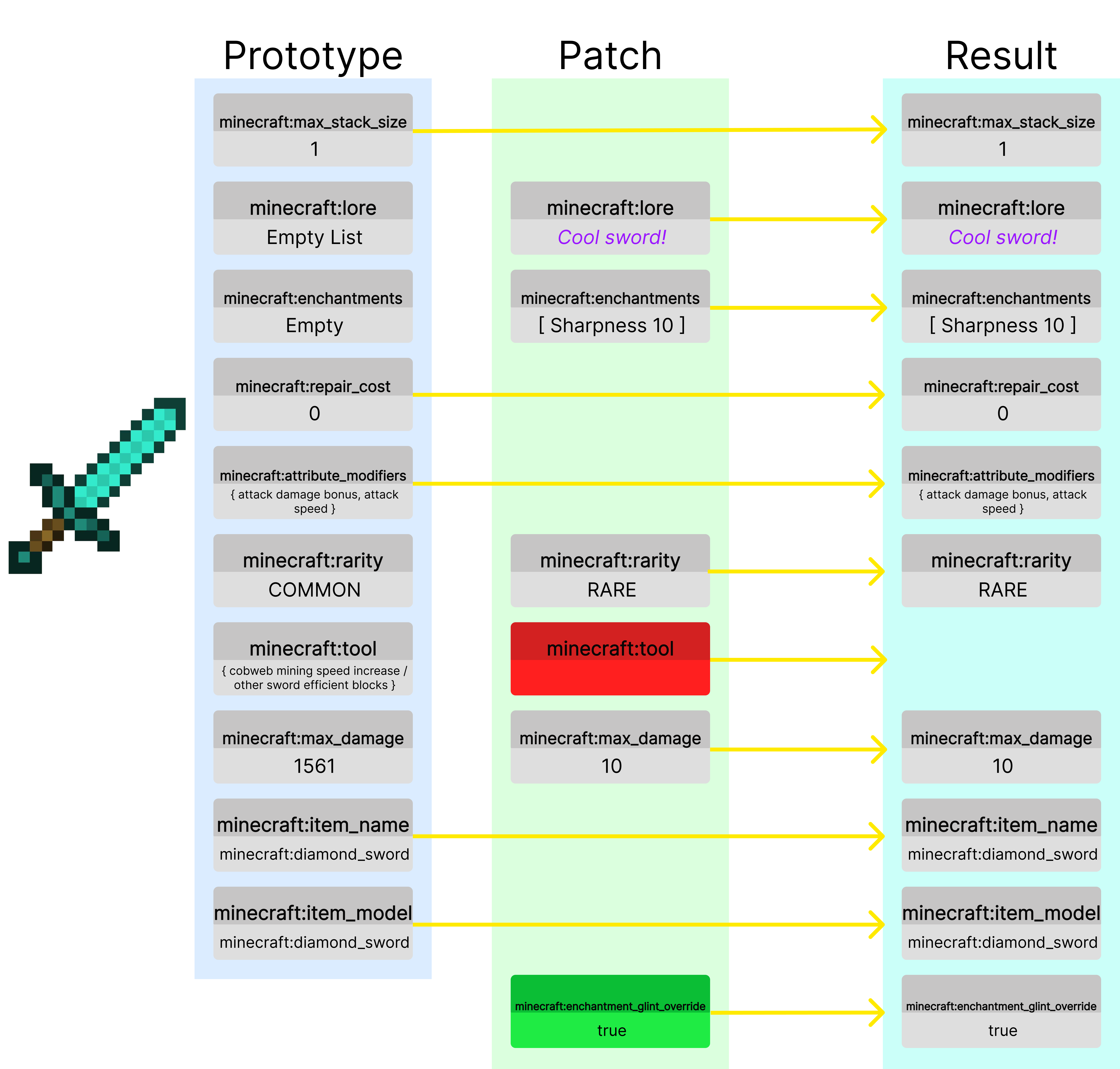 For implementation details, click here
For implementation details, click here
The prototype (default values)
Items come with an initial set of components that we call the prototype.
These components are defined on the ItemType of the ItemStack. They control the base behavior
of the item, representing a brand new item without any modifications.
The prototype gives items their initial properties such as if they are food, a tool, a weapon, etc.
The patch
The patch represents the modifications made to the item. This may include giving it a custom name, modifying the enchantments, damaging it, or adding to the lore. The patch is applied ontop of the prototype, allowing us to make modifications to an item.
The patch also allows for removing components that were previously in the prototype. This is shown by
the minecraft:tool example in red. We are removing this component, so this sword item will no longer
break cobweb or other sword blocks faster.
We can also add new components, as seen from the new minecraft:enchantment_glint_override component, which
allows us to make it appear as if it were enchanted.
Differences compared to ItemMeta
The ItemMeta API provides methods to modify ItemStacks in a hierarchical manner, such as CompassMeta, which allows you to modify the components of a minecraft:compass.
While ItemMeta is still very useful, it does not properly represent the prototype/patch relationship that Minecraft items use.
Key differences
Expanded data model
The DataComponent API exposes a much broader and more detailed set of item properties than ItemMeta.
Data components allow the entire item to be modified in a fashion that better represents how Minecraft does item modifications.
Version-specific
The DataComponent API is designed to adapt to version changes. The DataComponent API may experience breaking changes on version updates as Minecraft makes changes to components. Backwards compatibility is not promised.
Because ItemMeta is represented in a different format, breaking changes made to components by Mojang may not result in breaking changes to ItemMeta.
Builders and immutability
Many complex data components require a builder approach for construction and editing. All data types that are returned by the api are also immutable, so they will not directly modify the component.
Patch-only
ItemMeta only represents the patch of an ItemStack. This means that you cannot get the original properties (prototype) of the ItemStack, such as its default
durability or default attributes.
No snapshots
Currently, ItemMeta represents a snapshot of an ItemStack's patched map.
This is expensive as it requires the entire patch to be read, even values that you may not be using.
The DataComponent API integrates directly with ItemStack. Although conceptually similar, the DataComponent API focuses on explicit, strongly typed data retrieval and updates without this additional overhead.
When should I use DataComponents or ItemMeta?
You would want to use ItemMeta if you:
- Are doing only simple changes to
ItemStacks - Want to keep cross-version compatibility with your plugin
You would want to use data components if you:
- Want more complicated
ItemStackmodifications - Do not care about cross-version compatibility
- Want to access default (prototype) values
- Want to remove components from an
ItemStack's prototype
Basic usage
The DataComponent API will fetch values according to the behavior seen in game. So, if the patch removes the minecraft:tool component,
trying to get that component will return null.
Retrieving a prototype value
// Get the default durability of diamond sword
int defaultDurability = Material.DIAMOND_SWORD.getDefaultData(DataComponentTypes.MAX_DAMAGE)
Checking for a data component
// Check if this item has a custom name data component
boolean hasCustomName = stack.hasData(DataComponentTypes.CUSTOM_NAME);
logger.info("Has custom name? " + hasCustomName);
reading a valued data component
// The damage of an item can be null, so we require a null check
Integer damageValue = stack.getData(DataComponentTypes.DAMAGE);
if (damageValue != null) {
logger.info("Current damage: " + damageValue);
} else {
logger.info("This item doesn't have a damage component set.");
}
// Certain components, like the max stack size, will always be present on an item
Integer maxStackSize = stack.getData(DataComponentTypes.MAX_STACK_SIZE);
Setting a valued data component
// Set a custom model data value on this item
stack.setData(DataComponentTypes.CUSTOM_MODEL_DATA, CustomModelData.customModelData()
.addFloat(0.5f)
.addFlag(true)
.build()
);
Removing or resetting a data component
// Remove an existing component (e.g. tool)
stack.unsetData(DataComponentTypes.TOOL);
// Reset a component to the default (prototype) value for its item type (e.g. max stack size)
stack.resetData(DataComponentTypes.MAX_STACK_SIZE);
Non-valued data components
Some components are only flags and don't carry any sort of value:
// Make the item unbreakable
stack.setData(DataComponentTypes.UNBREAKABLE);
// Remove the unbreakable flag
stack.unsetData(DataComponentTypes.UNBREAKABLE);
Advanced usage with builders
Many data components have complex structures that require builders.
Modifying prototype component values
ItemStack itemStack = ItemStack.of(Material.DIAMOND_HELMET);
// Get the equippable component for this item, and make it a builder.
// Note: Not all types have .toBuilder() methods
// This is the prototype value of the diamond helmet.
Equippable.Builder builder = itemStack.getData(DataComponentTypes.EQUIPPABLE).toBuilder();
// Make the helmet look like netherite
// We get the prototype equippable value from NETHERITE_HELMET
builder.assetId(Material.NETHERITE_HELMET.getDefaultData(DataComponentTypes.EQUIPPABLE).assetId());
// And give it a spooky sound when putting it on
builder.equipSound(Registry.SOUNDS.getKeyOrThrow(Sound.ENTITY_GHAST_HURT));
// Set our new item
itemStack.setData(DataComponentTypes.EQUIPPABLE, builder);
This will create a diamond helmet that looks like a netherite helmet and plays a spooky ghast sound when equipped.
Example: Written book
ItemStack writtenBook = ItemStack.of(Material.WRITTEN_BOOK);
WrittenBookContent.Builder bookBuilder = WrittenBookContent.writtenBookContent("My Book", "AuthorName");
// Add a page
bookBuilder.addPage(Component.text("This is a new page!"));
// Add a page that shows differently for people who have swear filtering on
// Players who have disabled filtering, will see "I hate Paper!", while those with filtering on will see the "I love Paper!".
bookBuilder.addFilteredPage(
Filtered.of(Component.text("I hate Paper!"), Component.text("I love Paper!"))
);
// Change generation
bookBuilder.generation(1);
// Apply changes
writtenBook.setData(DataComponentTypes.WRITTEN_BOOK_CONTENT, bookBuilder.build());
Example: Cool sword
ItemStack itemStack = ItemStack.of(Material.DIAMOND_SWORD);
itemStack.setData(DataComponentTypes.LORE, ItemLore.lore().addLine(Component.text("Cool sword!")).build());
itemStack.setData(DataComponentTypes.ENCHANTMENTS, ItemEnchantments.itemEnchantments().add(Enchantment.SHARPNESS, 10).build());
itemStack.setData(DataComponentTypes.RARITY, ItemRarity.RARE);
itemStack.unsetData(DataComponentTypes.TOOL); // Remove the tool component
itemStack.setData(DataComponentTypes.MAX_DAMAGE, 10);
itemStack.setData(DataComponentTypes.ENCHANTMENT_GLINT_OVERRIDE, true); // Make it glow!
Matching items without certain data components
When comparing items, you sometimes want to ignore certain values. For this we can use the
ItemStack#matchesWithoutData
method.
For example, here we compare two diamond swords whilst ignoring their durability:
ItemStack originalSword = new ItemStack(Material.DIAMOND_SWORD);
ItemStack damagedSword = new ItemStack(Material.DIAMOND_SWORD);
damagedSword.setData(DataComponentTypes.DAMAGE, 100);
boolean match = damagedSword.matchesWithoutData(originalSword, Set.of(DataComponentTypes.DAMAGE), false);
logger.info("Do the sword match? " + match); // true